Dennis S. Schrock
Department of Horticulture, University of Missouri-Columbia
Shortcuts
Types of construction damage
Preventing damage
Tree care after construction
Tolerance of trees to root damage
Trees are a valuable asset in home landscapes. Their shade makes summer living more pleasant and can significantly reduce air conditioning costs. In winter, they shield against wind and snow, reducing heating costs. Leaves act as air cleaners, filtering dust and removing airborne pollutants. Trees shelter wildlife, slow rainfall runoff, muffle noise and provide privacy. But perhaps the main reason people value trees highly is simply the beauty and grace they add to a community.
Because it takes many years for a tree to grow to maturity, wooded building sites command premium prices. All too frequently, however, the trees that make the site attractive are damaged during construction. Trees may decline and die soon after construction work is finished. The homeowner then faces the cost of tree removal in addition to the expense and time needed to grow replacement trees.
Trees around older, established homes suffer from construction damage, too. Remodeling projects, sidewalk replacement, landscaping projects or utility work may cause injury to trees.
Types of construction damage
Damage to trees occurs directly from physical wounding or indirectly through change of environment around the tree.
Physical wounds
Careless movement of construction equipment causes wounds to tree trunks and root collars, the area of the tree at ground line where the roots begin to spread out. A healthy tree is capable of sealing off small wounds, localizing injury. However, large wounds and those on stressed trees will not readily seal off, allowing decay to begin.
Improper pruning to create clearance for construction equipment and tree removal techniques are other sources of physical injury to branches and trunks. As trees are removed for placement of a new building or driveway, they may scrape bark off trunks or break branches of trees that are to be saved. These wounds serve as entry points for diseases. Improper pruning leaves branch stubs that die and begin to decay. Make clean cuts with a sharp pruning saw just outside the swollen branch collar.
Below ground, root damage is common from excavation and grade changes. Roots may be torn by improper excavation, opening wounds for disease organisms to enter. Fine, absorbing roots are lost by topsoil removal, putting the tree under stress. Structural support is lost by trenching too close to major roots, creating a potential hazard. Bruising or crushing of roots by heavy equipment may not be apparent from above ground.
Environmental changes
Soil compaction is a serious problem on many construction sites. Even when care is taken to avoid trunk and branch injury from equipment, trees may be damaged by equipment driving over root systems. The weight of the equipment compacts soil, reducing air space in the root zone. Limited oxygen availability to roots is also a problem when soil is stockpiled at the base of trees or paving is put over existing roots.
Excessive thinning of tree stands or removal of underbrush causes increased exposure to sun, wind and heat. Sunscald may develop on trees previously acclimated to shade. Increased wind and heat exposure increases moisture stress.
Also, moisture stress may develop from grade changes that lower the water table or divert drainage patterns away from the site. On the other hand, excess soil moisture may develop from grade changes, as well. A rise in the water table, puddling from improper grading, or an increase in water flow through the area will decrease the amount of oxygen in the root zone and lead to tree decline.
Adding fill soil or cutting away excess soil alters the environment around tree roots. Hauling in fill reduces oxygen to the roots. Adding as little as 1 or 2 inches of heavy clay soil on top of the existing grade may damage sensitive trees such as oaks. The soil profile and soil pH are also altered. Topsoil is often more acidic than excavated subsoils spread on the surface. Trees adapted to growing in acidic topsoil will be stressed when forced to develop new roots in soil of a different pH and texture. Ability of roots to take up many micronutrients is reduced in high pH soils, leading to decreased growth rate and yellowing leaves. Construction material buried on-site also often raises soil pH.
Symptoms of damage
Symptoms of construction damage to trees appear over a period of several months to several years after the damage occurs. Because of the delay in development of symptoms, it is often difficult for people to understand the relationship between the earlier injury and the current symptoms.
The first symptoms to develop may be a slight wilting or shedding of a few leaves at the time of construction. Fall coloration often develops early and leaves drop prematurely. In later years, leaf size and shoot growth may be reduced. Twigs and branches die, and in the case of conifers, excessive needle drop occurs. General growth of the tree is slowed and resistance to diseases and insects is weakened.
Diagnosing compaction or root smothering damage can be difficult because it may take five to seven years for symptoms to appear. The speed and severity of symptom development depends on the amount of damage, the species of tree and soil type.
Deciding which trees to save
The first step in deciding which trees to save is to accurately mark out placement of proposed buildings, driveways, parking areas and utility routes. After marking these features, stand back to look over the site. A small shift in the position of the building, a change in driveway location, or altering the proposed utility line could make the difference between saving or cutting a valuable tree.
After deciding on building placement, prioritize trees for saving. Trees directly in the way of construction; undesirable, weedy tree species; trees already in a state of decline; or structurally hazardous trees should be marked for removal. If in doubt, consult a trained arborist, horticulturist, forester or nursery person to determine tree condition.
Next, determine which trees can be saved with little or no protection. Desirable trees located away from construction or traffic areas will survive if reasonable care is taken.
The final group of trees to examine are those that may survive construction, but only if proper measures are taken. Examine them more closely to determine if one of the techniques described below will effectively minimize damage. If severe damage is likely, it will be less expensive to remove the tree before construction begins than afterward.
Control traffic around trees
Tree roots are not mirror images of the tree top. Roots are concentrated in the top 12 to 18 inches of soil and spread two to three times the width of branches (see Figure 1). Protecting roots within the dripline of the tree is most critical, but damage to roots outside the dripline on only one side of the tree may remove one-third or more of the tree's roots (see Figure 2).
 |
Figure 1. Tree roots are not mirror images of the top branch structure (lower figure). While some trees do have deep tap roots, most do not. Roots spread to where soil conditions provide adequate moisture, aeration and nutrients. Typically, about 85 percent of a tree's roots are within the top 18 inches of soil (upper figure). |
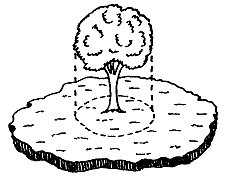 |
Figure 2. Roots typically spread out from two to three times the width of the branches. However, the essential roots are usually considered to be within the dripline, which is the area underneath the tree's branches. |
Erect a fence at the dripline or farther out, if possible, to prevent damage from excavation, soil compaction or stockpiling of soil over roots. It is easier to save groups of trees than individual ones. Build a fence around the dripline of the outside trees to keep construction machinery away from the grove. Remove protective fences only after all construction work is done, including final grading and smoothing of the site.
Carefully remove unwanted trees
Be careful removing unwanted trees. A tree being removed might fall on and injure one of the trees you plan to save. If possible, remove unwanted trees when none of the trees have leaves. When trees are in full leaf, sudden removal of nearby trees is a shock and can cause sunburn to other trees.
Make clean cuts
Clean cuts to roots seal off quickly and help prevent entry of disease-causing organisms. Ragged, rough wounds from dull or improper equipment allow decay to progress to the rest of the tree. Sharply cut ends promote a flush of new roots, helping the tree recover from injury. Bulldozers tend to tear roots apart, leaving wounds that will not seal readily. Trenchers and backhoes make cleaner cuts through the soil. When cutting roots larger than 2 inches in diameter, use a pruning saw to make a smooth cut.
Do not automatically prune the top of a tree that has been root pruned. As long as moisture is not limiting, leaves in the crown of the tree manufacture food to help roots grow and recover from being cut. Prune out only weak or dead branches.
Tunnel rather than trench
Trenching near a tree kills a large portion of the tree's roots. Tunneling under the tree does virtually no damage. Since most roots live in the top 18 inches of soil, a tunnel 2 feet deep often does little damage. However, placing the tunnel 3 to 4 feet deep is safer.
It is best to tunnel at least 1 to 2 feet away from the tree's center to avoid a tap root (see Figure 3). For trees under 6 inches in diameter at breast height, trenching should come no closer than the dripline of the tree. See Table 1 for larger trees.
 |
Figure 3. Trenching near a tree can kill almost half its roots. A tunnel in the same place will do virtually no damage to the tree. |
Table 1. Minimum distance to trench trees. (Adapted from Municipal Foresters of Northeastern Illinois guidelines.)
|
Tree diameter at breast height |
Minimum distance from tree to start tunneling |
|---|---|
|
less than 6 inches |
dripline of tree |
|
6 to 9 inches |
5 feet |
|
10 to 14 inches |
10 feet |
|
15 to 19 inches |
12 feet |
|
more than 19 inches |
15 feet |
Prevent soil compaction
Where fencing to prevent construction traffic is not possible, use temporary wood chip mulch, gravel mulch or bridges to prevent soil compaction around tree roots. Place wood chips or gravel mulch 6 to 12 inches deep on top of a geotextile landscape fabric placed over the root zone of the trees to be protected.
Air spaces in the mulch cushion the impact of machinery or foot traffic and disperse the weight over a larger area. The landscape fabric makes cleanup easy. Temporary bridges built from steel plates placed on railroad ties distribute the weight of equipment over larger areas. What compaction does occur will be limited to areas directly below the railroad ties (see Figure 4).
|
|
Figure 4. Use of bridges to protect tree roots. |
Handle grade changes
Cutting away soil from a tree removes a portion of the root system and changes the soil moisture level. For reasonable survival of trees, make no cuts within the dripline. Construct a retaining wall at the dripline or farther out to preserve the tree's roots (see Figures 5 and 6).
|
|
Figure 5. This change in grade has killed half the tree's roots. Most trees will die from this extent of injury. |
 |
Figure 6. The tree on this cut has been protected by a curved retaining wall at the dripline. The tree should recover nicely. |
Filling around trees smothers roots. Build a retaining wall at the dripline to keep soil from burying roots within the dripline. It is possible to completely cover the roots by using expensive drainage and venting techniques that require professional design and installation. It is easier, cheaper and more practical to alter grading plans than it is to protect a tree from fill over the entire root zone.
With proper care, trees moderately affected by construction damage will recover. Homeowners can help trees recover by practicing annual tree care as outlined in the following:
Aerate the soil. Pull out cores of soil 12 to 18 inches deep to aid movement of oxygen and moisture into soil and help combat compaction. Fertilizer may be placed in the holes. Use compost to backfill the holes. New roots quickly fill in the cores.
Water deeply. During dry periods, moisten the root zone of stressed trees. Let the water soak in 12 to 18 inches deep by applying a slow trickle throughout the spread of the tree's roots.
Inspect the tree for damage. Stressed trees are more susceptible to disease and insect attack. Check them frequently to catch pest problems before they become severe. Treat with a pesticide, if necessary. Prune out any dieback that develops.
Mulch. A 2- to 4-inch layer of mulch around the base of trees helps prevent soil compaction, reduces weed competition and conserves soil moisture. Keep the mulch away from the tree trunk to prevent collar rot from developing.
Fertilize. Severely stressed trees should not be fertilized until they become re-established a year or two later. Young, rapidly growing trees should be fertilized annually. Mature trees may be fertilized every two or three years. Using a complete fertilizer, apply 2 pounds of actual nitrogen per thousand square feet. Fertilizer may be spread over the soil surface or distributed among aeration holes punched 12 inches deep every 2 feet under the tree's canopy.
Tolerance of trees to root damage
Not all trees are equally sensitive to soil-related construction injury (see Table 2). Some can generate new roots quickly when conditions become unfavorable for the old roots. This adaptation occurs primarily in species that grow in river bottom flood plains. Tree species native to upland sites are less likely to adapt to soil grade changes or construction damage.
Table 2. Tree tolerance to root damage, by species.
|
Very sensitive |
Moderately sensitive |
Fairly tolerant |
|---|---|---|
|
Oaks |
Sugar maple |
Silver maple |
|
Hickories |
Ash |
Basswood |
|
Honeylocust |
Walnut |
Cottonwood |
|
Kentucky coffeetree |
Sycamore |
Poplar |
|
Horse chestnut |
Hackberry |
Willow |
|
All conifers |
Red maple |
River birch |
|
Redbud |
Hawthorn |
|
|
Serviceberry |
Ironwood |
|
Trees are a valuable asset in the landscape and should be protected during construction. With careful planning and forethought, desirable trees can be saved and the disappointment of delayed tree decline prevented.
Copyright 2000 University of Missouri. Published by University Extension, University of Missouri-Columbia